EconStor Survey 2022: Repository Registers Satisfied Users, but More Marketing Efforts Needed
More than 13 years ago, the ZBW launched its repository EconStor. In 2022, the team conducted a survey among its users. In this article, three team members share the most interesting results, insights into user behaviour and starting points for making the repository even better.
by Ralf Toepfer, Lisa Schäfer and Olaf Siegert

Back in 2009, the ZBW launched its disciplinary Open Access repository EconStor. Now in 2022, it provides more than 240,000 academic papers from the economics and business studies disciplines, coming from over 600 institutions and about 1000 single authors worldwide. All papers are available in Open Access. After thirteen years of developing and connecting EconStor we thought, it was high time to hear from our research community, what they think about the repository and its services.
In this short report, we would like to present the results of a user survey we conducted this year. First, we will give some background information about the survey and how it was conducted. Then we describe who the actual respondents were. Last but not least, we present some results on specific aspects of the survey.
Background information
The idea to conduct a survey came up in a brainstorm meeting of the EconStor team in 2020. Our aim was to address the following topics:
- Satisfaction of the research community with EconStor,
- Environment analysis (which other tools are used in economic research?),
- Special look at our authors (who is uploading papers on EconStor?),
- Suggestions for further development.
Since we are no survey experts, we knew, we would have to rely on some external assistance. This was provided from two sides: First, our ZBW marketing team, who had conducted surveys on other issues before. And second, from a course of students in library and information science at the HAW -Hamburg University of Applied Sciences (German). Their professor, Petra Düren, contacted us in spring 2021 to ask for practical examples regarding user surveys. We decided to organise an international EconStor user survey together at the start of 2022. We developed the questionnaire and used Limesurvey as our tool for the survey. After some pretesting, we were ready to start.
The survey was conducted between the 10th and the 24th of January 2022. We promoted it via the EconStor website and through mailings among researchers in Germany and abroad. Overall, we received 756 responses, of which 441 were fully completed questionnaires.
Profile of respondents
Most of the respondents came from Europe (87%): Half of them (45%) was based in Germany, other major European countries were Italy (16%), Spain (5%) and France (4%). From the rest of the world about 3% overall came from the United States and 3% from Australia.
Regarding their affiliations, most respondents were coming from universities (78%), another 10% were from universities of applied sciences and 6% from non-university research organisations. The rest mainly came from central banks or the private sector.
With regard to the age of the participants, we received fairly even answers from different age groups according to the academic career span: i.e. 9% were younger than 30 years, 45% were between 30 and 49 years and 56% were 50 years or older. Looking at their academic status, 58% were professors, 20% were researchers or postdocs and 18% were PhD Students (see illustration 1).
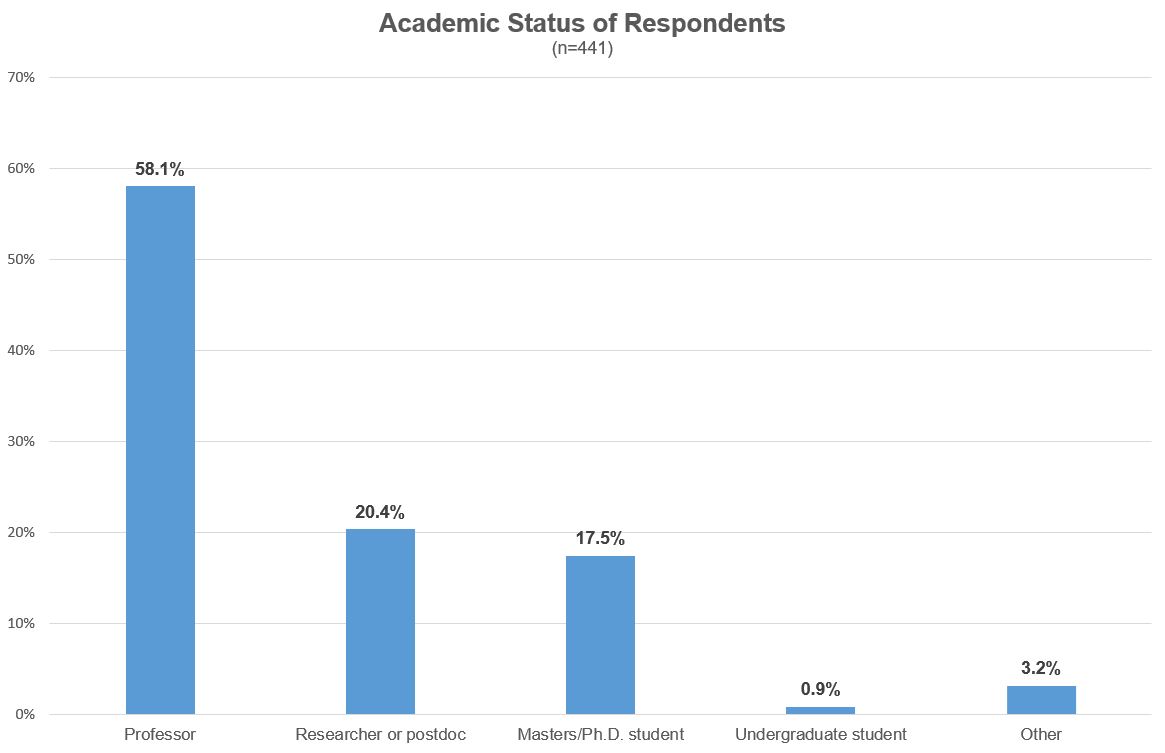
Illustration 1: EconStor User Survey 2022: Participants by academic status
Regarding the scientific disciplines, most of the respondents came from the field of economics (65%) or business studies (25%), the remaining 10 % were allocated to neighbouring disciplines such as sociology, political studies, statistics or geography.
Results of the EconStor survey
The survey addressed various aspects of the use of EconStor such as awareness and familiarity of the services, usage of searching and browsing options, evaluation of the services and suggestions for improvement. In the following, we briefly present some key results.
Usage & environment analysis
The majority of respondents have known EconStor for more than three years, but there are differences by discipline, as researchers in economics are aware of EconStor longer than their colleagues in business studies (see Illustration 2).
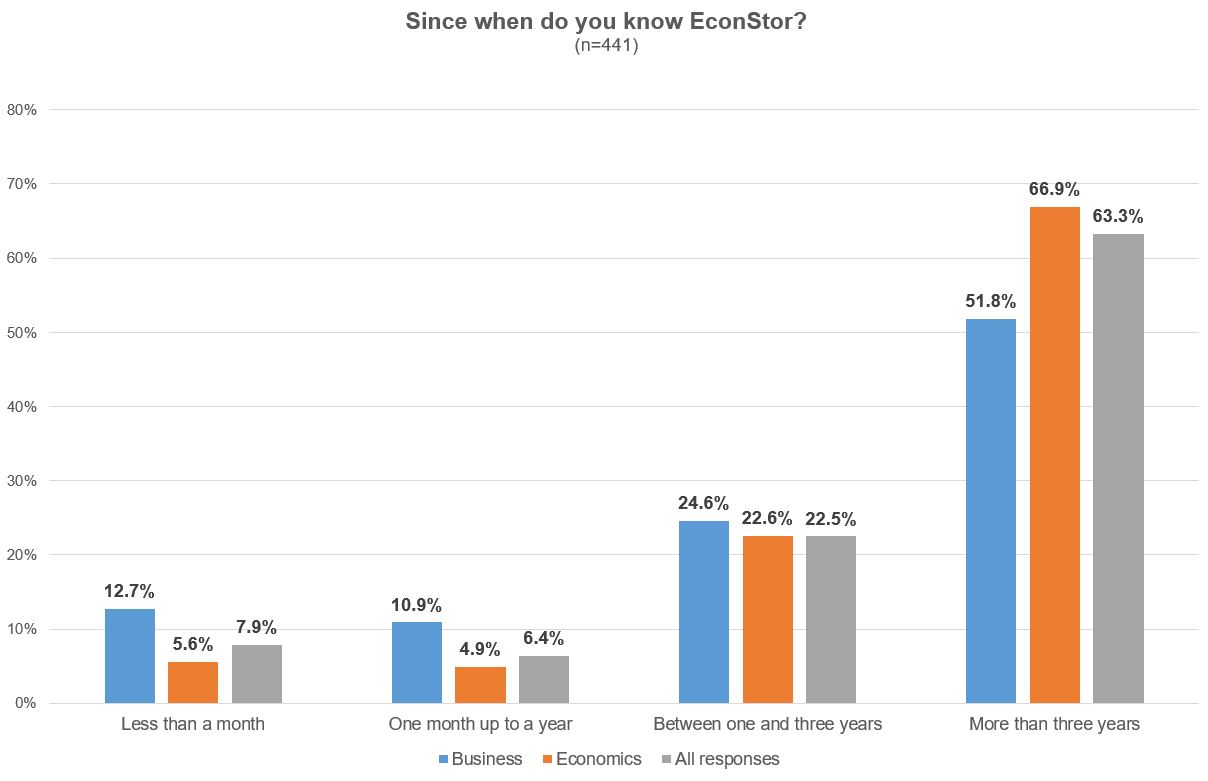
Illustration 2: EconStor User Survey 2022: Awareness of EconStor
In terms of usage, almost half of the respondents use EconStor at least once a month and about 14% even weekly, indicating that the majority of respondents are quite familiar with the platform.
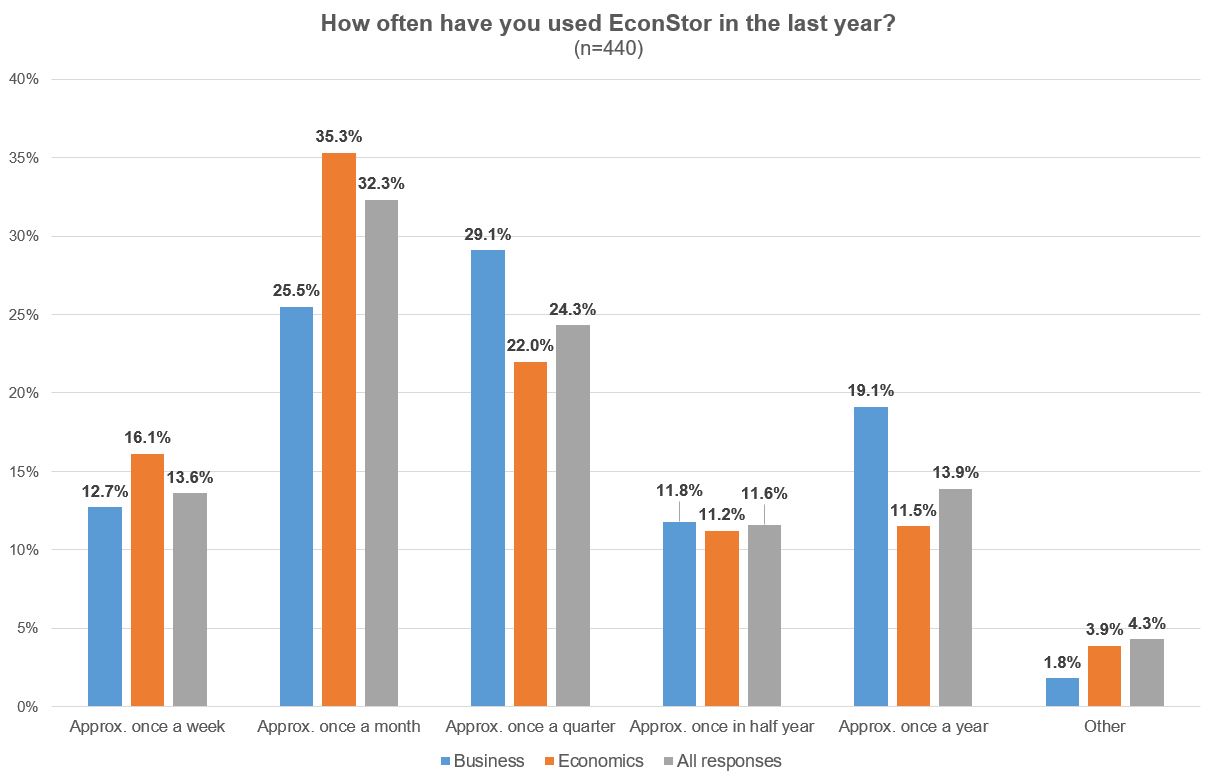
Illustration 3: EconStor User Survey 2022: Usage of EconStor
About one third of the respondents from the field of economics first discovered EconStor via RePEc, while most researchers from business studies became aware of EconStor via Google Scholar. This is in line with the answers given concerning the use of other platforms the researchers use to access economic papers, where besides ResearchGate, Google Scholar, RePEc and SSRN are mentioned.
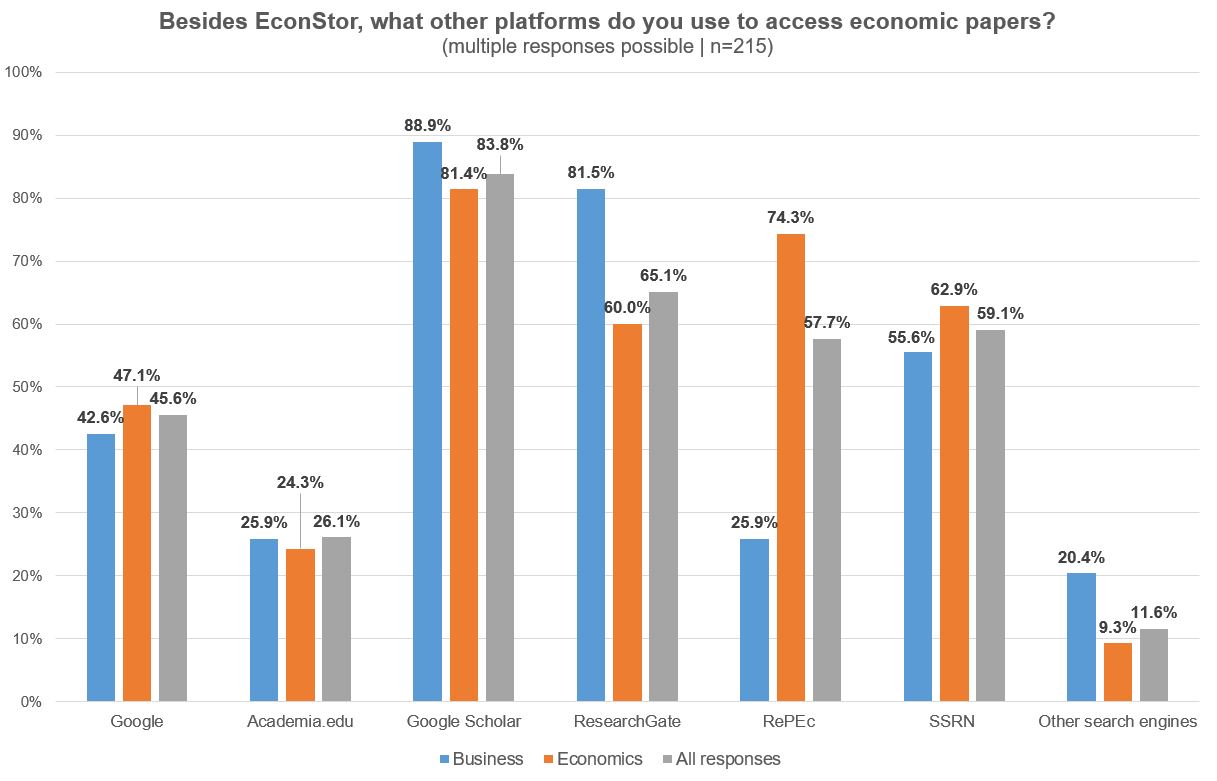
Illustration 4: EconStor User Survey 2022: Usage of other platforms than EconStor to access economic papers
Coincidently ResearchGate and to a lesser extent RePEc and SSRN are the most used platforms to distribute research papers in economics and business studies. Researchers also consider their own research institution important for disseminating their papers. This suggests that institutional repositories are still relevant even if large disciplinary and interdisciplinary platforms exist.
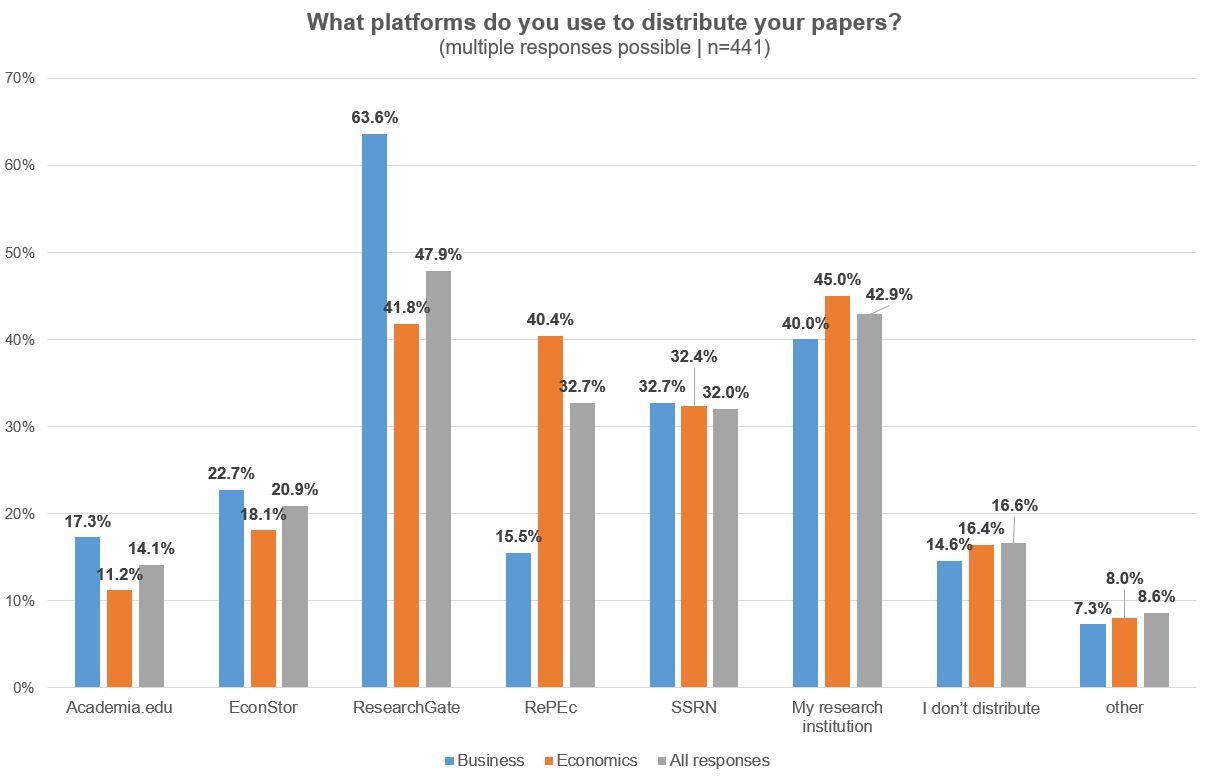
Illustration 5: EconStor User Survey 2022: Platforms to distribute research papers
Searching & browsing
EconStor provides several options to navigate through the website. Users can find papers by searching specifically for individual titles or by using the browsing function to view documents sorted by institution, type of document, author, etc. Considering the answers given, searching and browsing options are not very important. Only about 50% of respondents even use the options provided by EconStor. One of the respondents wrote, “I search for papers mostly via Google or Google Scholar, where I may find EconStor papers. It did not occur to me to search on EconStor itself, or to explore its functionality.” This answer seems to describe the typical use case of EconStor accurately. Our monthly usage statistics tell the same story: Researchers use EconStor primarily as a source to get the full text after searching databases or using search engines.
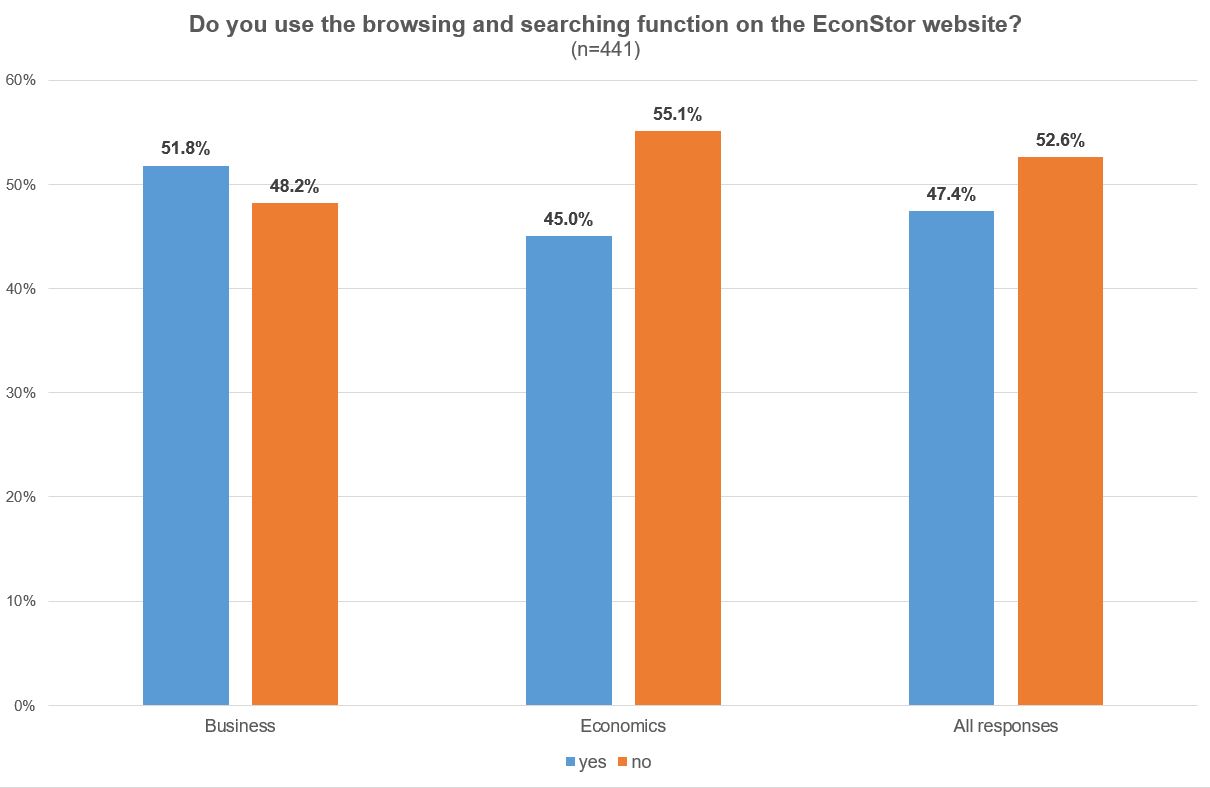
Illustration 6: EconStor User Survey 2022: Usage of browsing and searching functions
Self-upload & quality management
More than 600 institutions use EconStor to disseminate their publications. Authors can also upload their papers themselves, although this feature is reserved for Ph.D. researchers in economics and business studies at academic institutions. After registering, authors can upload working papers as well as journal articles, book chapters, conference proceedings, etc. The majority of about 55% of the respondents did not know about this option. However, of the authors who actively use the self-upload feature, more than 95% are satisfied or even very satisfied with the self-upload process.
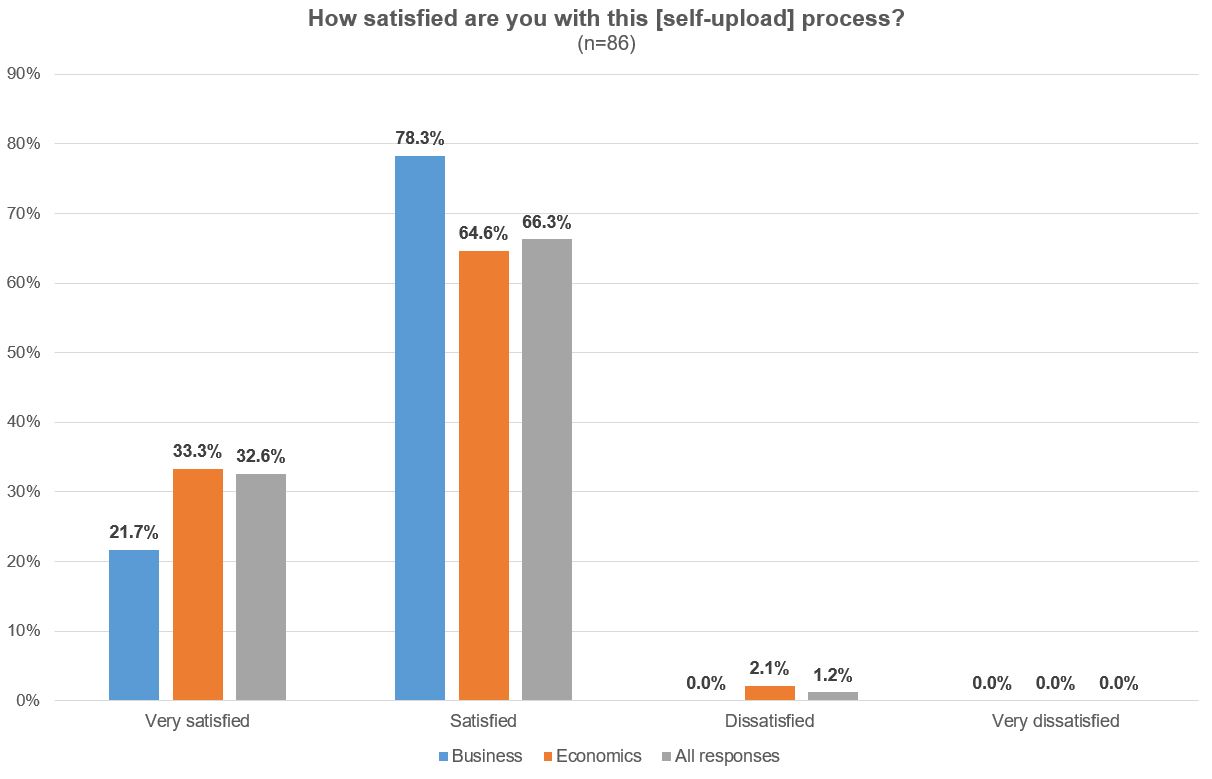
Illustration 7: EconStor User Survey 2022: Satisfaction with the self-upload process
Once a paper is uploaded, the EconStor team checks several points for quality assurance: namely plagiarism check, personal requirements for registration, document type, journal listing in Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) and formal checks of the paper. About two thirds of the authors appreciate this quality assurance measures. The plagiarism check and formal check are most important to them.
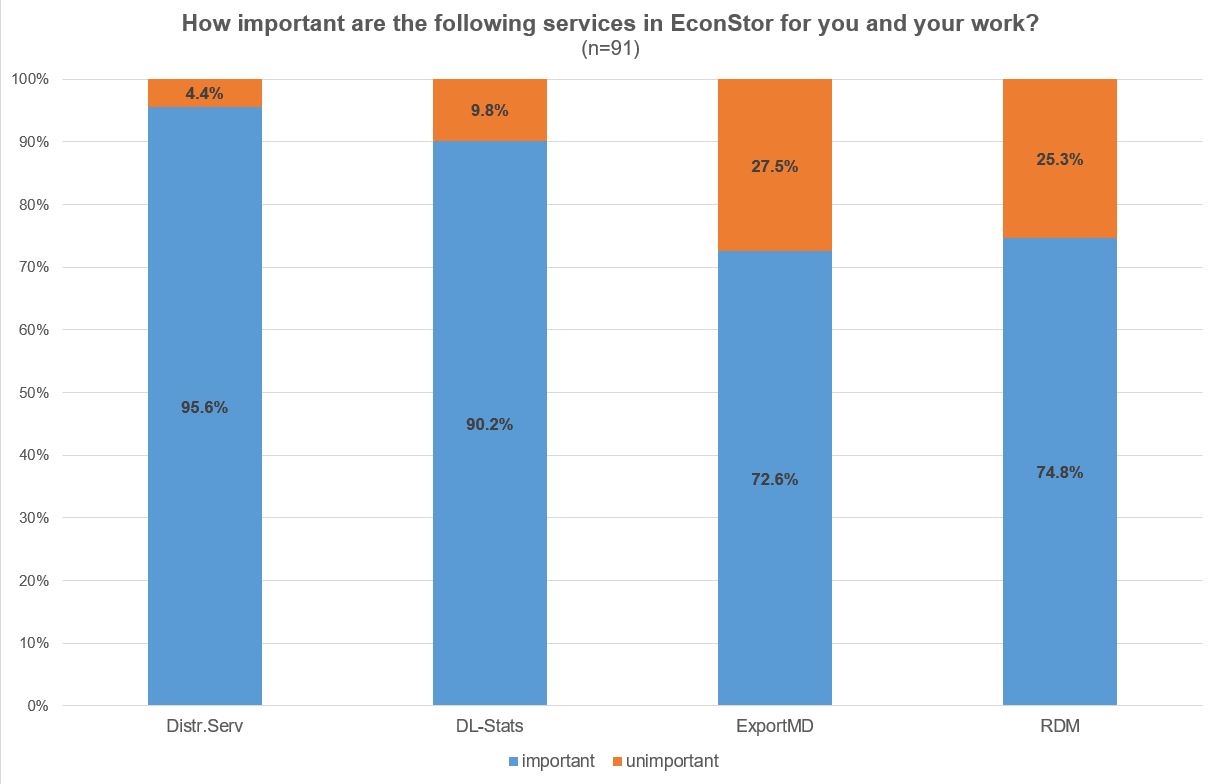
Illustration 8: EconStor User Survey 2022: Importance of quality assurance checks
Evaluation of other EconStor services
EconStor provides some more services than the self-upload feature or the searching and browsing options. To the EconStor users the most important other services are the distribution service and the provision of download statistics. The distribution service includes distribution to search engines like Google, Google Scholar or BASE (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine) and to academic databases like WorldCat, OpenAire and EconBiz . More than 90 % of the respondents agree that these two services are important for their work. The possibility to export metadata and to link papers with their underlying research data are relevant too, but to a lesser extent.
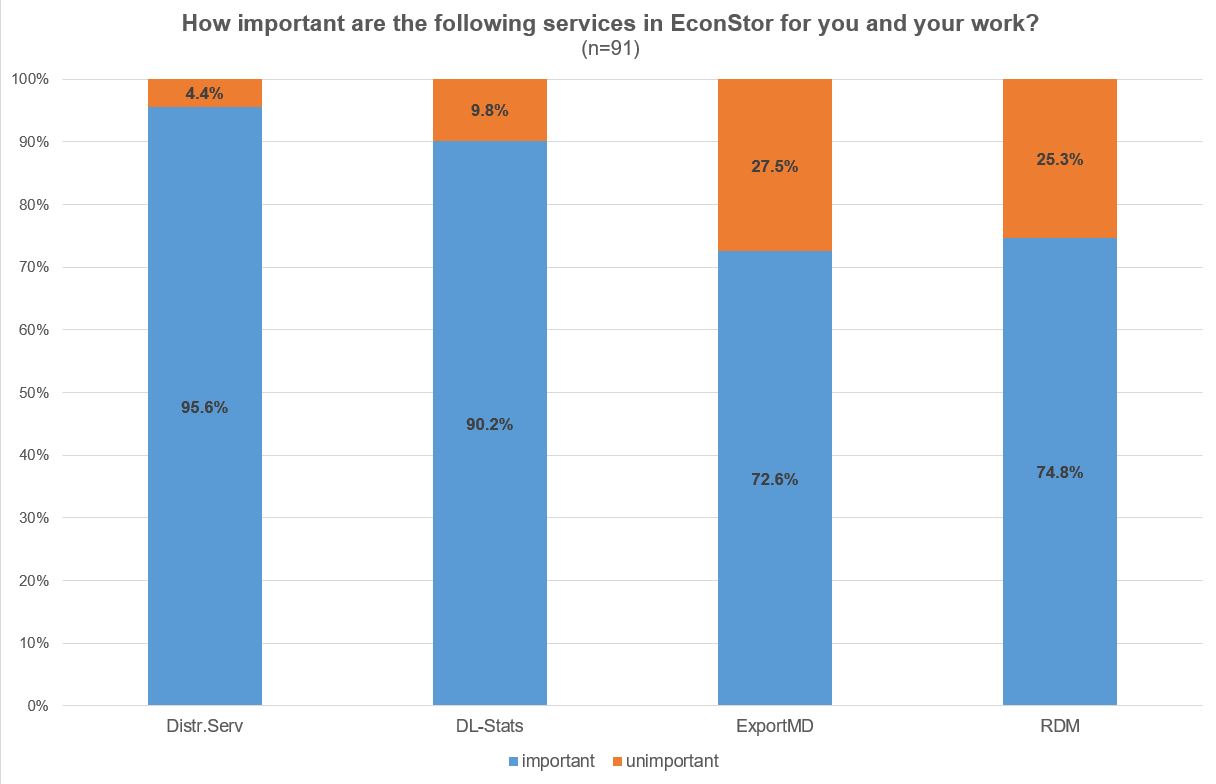
Illustration 9: EconStor User Survey 2022: Importance of different services in EconStor
Overall evaluation of EconStor
More than 95% of the respondents are satisfied or very satisfied with EconStor and its services overall. This applies to the two research areas of economics and business studies.
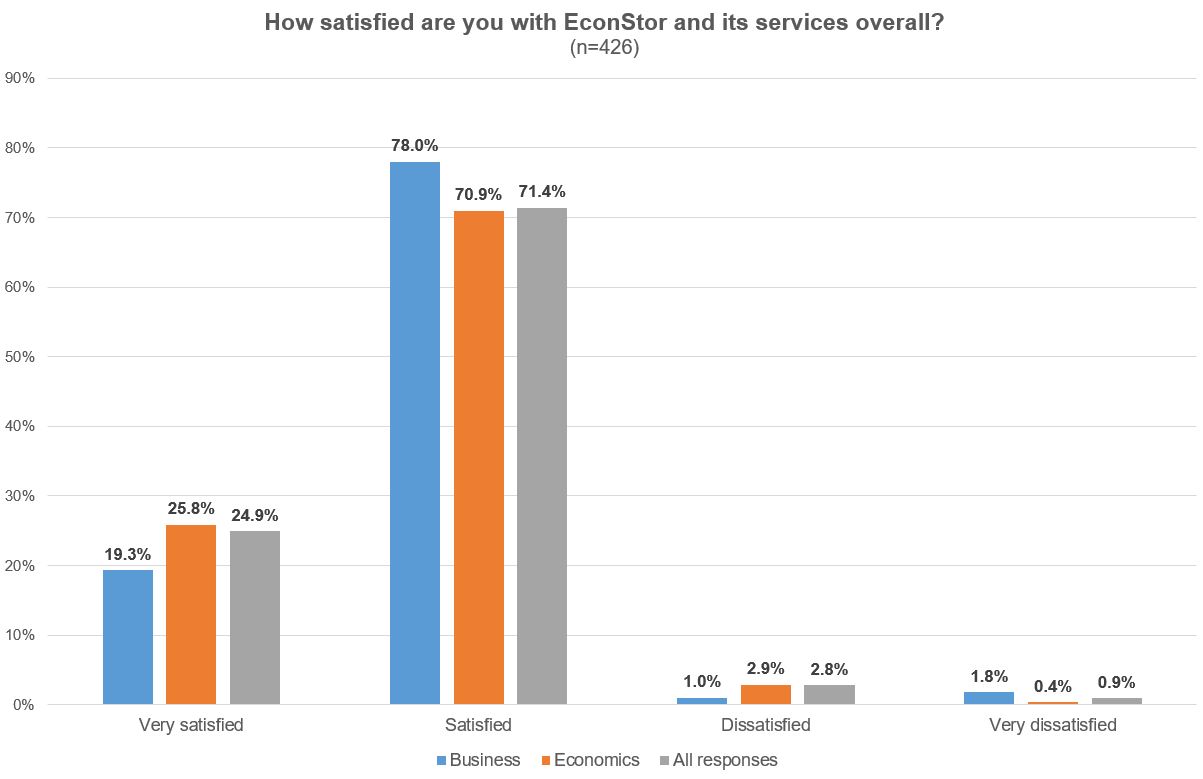
Illustration 10: EconStor User Survey 2022: Evaluation of EconStor and its services overall
About 67% of the respondents feel sufficiently informed about the services on the EconStor website. While this is by no means a bad result, there is room for improvement. Some respondents for example suggest providing a newsletter informing about new content indexed in EconStor.
Suggestions for improving EconStor
54 respondents were kind enough to share their views on possible improvements to EconStor. The suggestions ranged from the desire for higher visibility or awareness of EconStor and the desire for more information about the product to suggestions for improving individual functions.
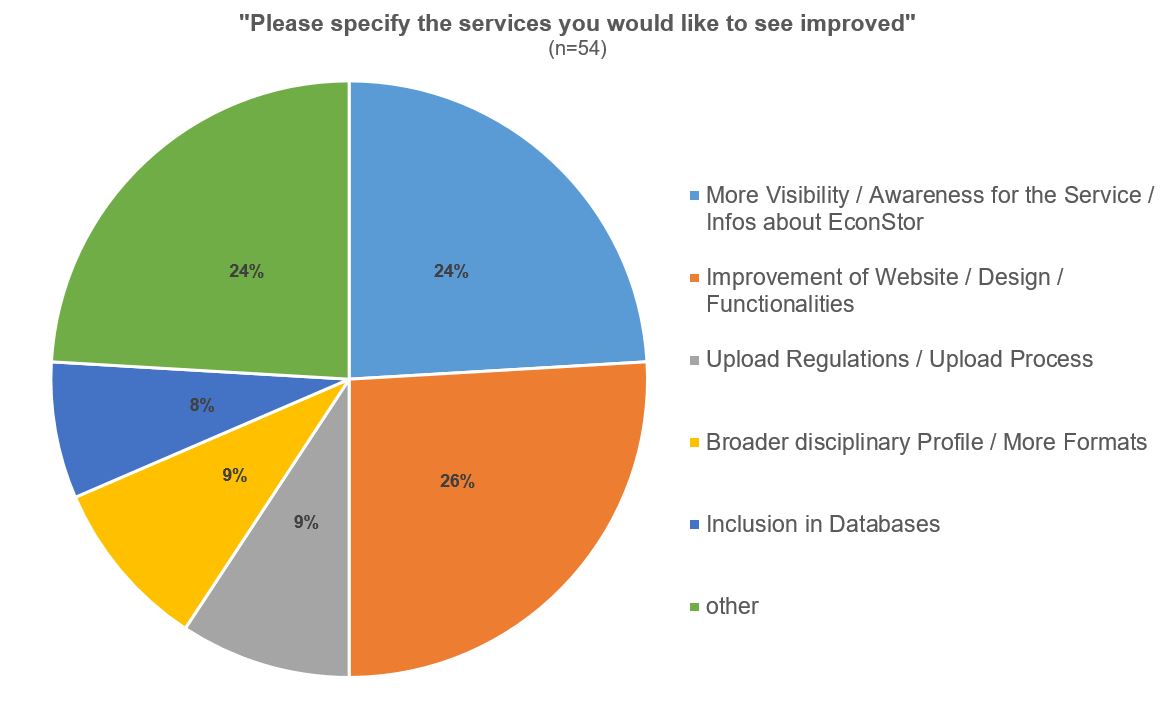
Illustration 11: EconStor User Survey 2022: Suggestions for improving EconStor
Conclusions on the 2022 EconStor survey
Overall, the researchers evaluated EconStor very positively. In particular, users who have known the service for several years and those who actively use the self-upload feature are very satisfied with it. Its users perceive EconStor primarily as a full-text source that can discovered via search engines, while its own search and browsing functions are less well known. The environment analysis shows differences between researchers from economics on the one side and business studies on the other, e.g. regarding the relevance of RePEc or ResearchGate. The potential for greater use could be tapped through stronger marketing (including promotion of the self-upload service) and through supplementary services.
The EconStor team very much appreciates the answers and opinions provided. This will help us to make EconStor even better. As a first response, we have created two promotional videos, one regarding EconStor in general, and the other one regarding the self-uploading process in particular. Other improvements will follow soon.
This could also interest you:
- EconStor Website
- Video: EconStor in general: Key facts about EconStor
- Video: Self-uploading process: How to upload a paper to EconStor
- Publishing in Repositories
- Open Access: Is It Fostering Epistemic Injustice?
- Third-Party Material in Open Access Monographs: How Far-Reaching is the Creative Commons Licence Really?
- Science Checker: Open Access and Artificial Intelligence Help Verify Claims
- Interview: Open Access Preprints Boost Article Citations and Mentions
- Academic Journals: How Open Access, Peer Review and the like are Shaping New Journal Concepts
- Executive Summary on the Use and Importance of Repositories (German, PDF)
- Video: Second Publication Rights for Researchers (German)
- Repositories as Tools for Comprehensive Research Data Management (German)
- Repositories, Usage Data and Statistics (German)
About the authors:
Ralf Toepfer works in the Publication Services department of the ZBW – Leibniz Information Centre for Economics, where he is responsible for discipline-specific services for the management of economic research data, prepares publication analyses in the context of the Open Access transformation and supports the development of the Open Library Economics (OLEcon). He can also be found on Mastodon.
Portrait: ZBW©, Photographer: Sven Wied
<Lisa Schäfer has been supporting various Open Access transformation projects at the ZBW – Leibniz Information Centre for Economics since 2020.
Portrait: Lisa Schäfer©
Olaf Siegert is head of the Publication Services department and Open Access Representative of the ZBW – Leibniz Information Centre for Economics. He is involved with open access as part of his work at the ZBW and is also active for the Leibniz Association, where he represents the Leibniz Open Access working group in external committees. He is involved in the Alliance of Science Organisations in the working group Scientific Publication System and at Science Europe for the Leibniz Association.
Portrait: ZBW©
View Comments

Self-organised network: does Mastodon have what it takes to become the “scholarly-owned social network”?
A “scholarly-owned social network” as an alternative to the major commercial players...



